WEBER VS RINNE TEST
Difference between sensory neural hearing loss and conductive hearing loss
The difference between sensory neural hearing loss and conductive hearing loss is also high yield if you look in first aid
this only gets a little table in first aid but many students report that this
does show up a lot. So it's important to know here is a really simplified
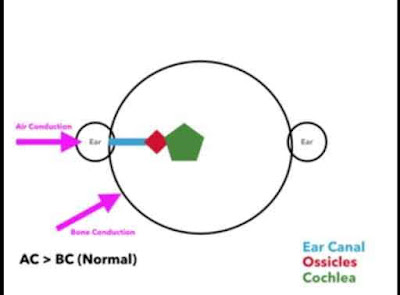
drawing of the heating system you have two ears, in this case, they look like
little Mickey Mouse ears. Then you have a blue ear canal some red ossicles and
a green cochlea I've labeled that for you hereby colors just so we can keep
this really simple there are two types of ways that we conduct impulses to be
able to process them through cranial nerve eight one is through air conduction.
If something is held right in front of your ear it moves through the air into
your ear and is conducted on its way towards the brain the other is bone
conduction if something is held against the bony process of the skull.
Difference
between Weber and Rinne test
Sound waves move through the bones and go directly to the cochlea under normal circumstances “air conduction is greater than bone conduction” this makes sense if something is held right next to your ear it's gonna be louder and more audible than if it was held against your skull now, let's say that we place a tuning fork on the mastoid the process you need to know whether this is the Weber test or the Rinne test the mnemonics remember this is that the Rinne is under the penny so if you know that the outside of the ear is called the pinna or the penny ready under the penny so anything that's under the ear it's there ready because your Rinne is under the penny, so what you do is you strike the tuning fork and you put it under the penny or on the mastoid process and then you ask the patient to tell you when they can hear it they tell you that they can hear it and then you move it right outside the ear.
 |
So what you've done at first is you've tested
bone conduction with Rinne under the penny and then you've moved it right
outside the ear to test air conduction again under normal circumstances. Air
conduction should be greater than bone conduction if they have conductive the hearing loss they'll be able to hear it better when it's held against the bone
when it's under the penny on the mastoid process but our mnemonic to remember
the Rinne test is Rinne under the penny there's another test that you have to
know if you place the tuning for if you strike the tuning fork and place it on
the top of the patients head this is the weber test localizes ears the Weber test tells you, Weber, it's the right or left ear see what I did there I
replace the word weather with Weber so the Weber test tells you, Weber,
it's the right or the left ear when you strike a tuning fork and place it on
their head during the Weber test the sound moves to both ears. So this is for
localization under normal circumstances the patient should be able to hear
the sound equally in both ears but if they have sensory neural hearing loss
they're not going to hear it in the ear that has sensory neural hearing loss
which means it localizes to the good ear in other words if I strike a tuning
fork and do the weber test and place it on your head and you only hear it in
your left ear which means that your right ear has sensory neural hearing loss.
so Rinne under the penny and a Weber tells you whether it's right or the left so that's a lot of information in a very short amount of time so why don't we do an example if a tuning fork is placed on the mastoid and then moved outside the right and left ears the patient says that they're able to hear the tuning fork better when it's held in the air next to both ears. The physician then strikes the tuning fork and places it on the patient's head the patient says that they hear the tuning fork better in their right ear what is the diagnosis.
So
I'm asking you what type of hearing loss is present if at all so let's dissect
this step by step the first thing that the physician did was strike the tuning
fork place it on the mastoid and then move it outside both ears he started with
the mastoid that's Rinne under the penny so he did Rinne under the penny and
the patient said that they were able to hear the tuning fork better when it was
held in the air that's a normal response because again air conduction should be
greater than bone conduction, so we have a normal for any test then the
physician strike the tuning fork and placed it on the patient's head what test
is that. Well that's the Weber test it told you Weber was the right side of the
left side. When the physician did this the patients and that they were able to
hear the tuning fork better in their right.
The question is which ear has sensory neural
hearing loss and that is the left because the patient heard it better on the right
side so here that was just a really easy example but it goes to show you how
simple these tests are if you know what the tests are testing for in a nutshell
if I'm gonna summarize all this for you I would say that the Rinne test is
really under the penny, you put it on the mastoid just below the pin of the ear
and you're testing for conductive hearing loss the Weber test is testing for
sensory neural hearing loss it tells you, Weber, it's the right side or left
side that has sensory neural hearing loss these are very high yield and me
suggest that you go through this post once or twice to get it down it should
only take you five minutes but it will be free points on test day if you
dedicate the necessary amount of time.
 Reviewed by yogiblogs
on
May 15, 2020
Rating:
Reviewed by yogiblogs
on
May 15, 2020
Rating:








No comments: